Eye Bleeding (Hyphema): Definition, Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors and Treatment
Published on December 15th, 2025
 Canada
Canada
Eye bleeding is a common term that may refer to several types of bleeding in the eye. Hyphema specifically is a type of eye bleeding characterised by bleeding inside the eye between the cornea and iris. This article will explore the eye bleeding or hyphema symptoms, hyphema causes, risk factors and hyphema treatment. The symptoms of eye bleeding or hyphema are blood in the eye, sensitivity to light and eye discomfort. Hyphema eye bleeding may be caused by trauma or injury to the eye, medical conditions or eye surgery. Treatments can include elevating the head, resting and covering the affected eye. Risk factors for eye bleeding or hyphema are playing sports, diabetes, blood-clotting disorders and some blood-thinning medications. Hyphema is a serious condition and it is recommended to seek immediate medical attention if you believe you may have hyphema. It is important to note that Oscar Wylee does not provide emergency medical treatment for hyphema or eye injuries. For urgent or emergency eye bleeding, seek immediate care at a hospital or emergency medical service.
What is Eye Bleeding?
Eye bleeding refers to several conditions in which there is bleeding in the eye. Hyphema specifically refers to bleeding inside the eye, specifically in the anterior chamber of the eye, which is between the cornea and the iris. Hyphema is most commonly caused by trauma to the eye or underlying medical conditions. According to James Gragg, Kyle Blair, and Mari B. Baker in a paper published in the National Library of Medicine, a bleed in the eye is classified as a hyphema if the blood is clearly visible to the naked eye or via inspection by a slit-lamp.
Eyes Bleeding Meaning
Eye bleeding refers to several types of eye bleeding, such as hyphema or a subconjunctival haemorrhage. Hyphema is bleeding in the eye where blood pools inside the eye, in the anterior chamber. A subconjunctival haemorrhage is caused by broken blood vessels under the conjunctiva, the membrane layer covering the surface of the eye and inner eyelids.
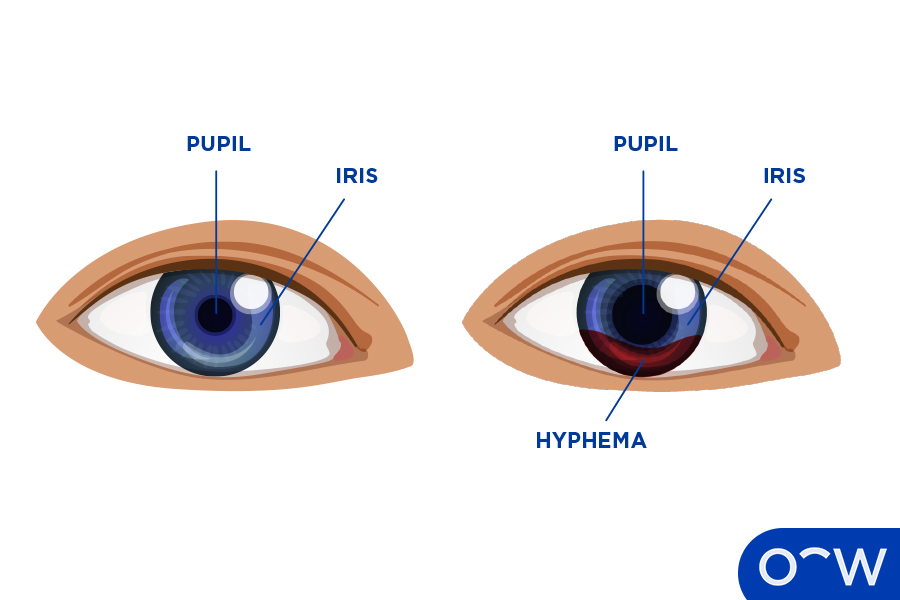

What are the Other Terms for Eye Bleeding?
The other term for bleeding inside the eye is hyphema, which is a medical term.
How Does Eye Bleeding Develop?
Hyphema, or bleeding in the eye, commonly develops after blunt trauma to the eye. Some medical conditions may also cause hyphema. Hyphema is a result of injury to the blood vessels in areas like the iris and ciliary body caused by trauma or a medical condition, according to MyHealth Alberta. The injury to these blood vessels, which can include tearing, leads to blood pooling in the layers of the eye, particularly the outer layer, which is the cornea and the iris, which is the coloured part of your eye.
How Common is Eye Bleeding?
Hyphema, or bleeding in the eye, can affect anyone, but it is more common in younger people after sports or recreational-related eye injuries. According to Ento Key,
What are the Causes of Eye Bleeding (hyphema)?
The causes of hyphema, or bleeding in the eye, include trauma or injury to the eye, medical conditions and eye surgery. Medical conditions that cause hyphema are sometimes known as spontaneous hyphemas, whereas those caused by a hit to the eye are more commonly known as traumatic hyphemas. What causes bleeding in the eye in the case of trauma is an injury to the blood vessels in the iris and ciliary body parts of the eye, also known as the anterior chamber, which leads to blood leaking into the space between the cornea and the iris. Damage to the blood vessels in the eye commonly results from trauma to the eye, received by a hit to the face. The hit to the face that causes hyphema may occur during sports such as basketball or boxing, a fight or other accident. Medical conditions and ocular surgery may also cause damage to the blood vessels and bleeding in the eye. Some causes of eye bleeding, or hyphema, are listed below.
- Trauma or injury to the eye: One of the most common causes of bleeding inside the eye, or hyphema, is trauma or injury to the eye. Trauma or injury to the eye that causes hyphema is generally caused by a hit to the eye. The hit to the eye that causes hyphema can be received during activities such as sports like basketball, rugby, boxing or soccer, recreational activities, fights or other accidents. A hit to the eye can cause trauma to the blood vessels in the iris and ciliary bodies, resulting in bleeding.
- Medical conditions: Causes of blood in the eye also include medical conditions. According to James Gragg, Kyle Blair, and Mari B. Baker in a paper published in the National Library of Medicine, people who have medical conditions such as eye tumours, diabetes, clotting disorders or sickle cell disease may be predisposed to issues such as vascular abnormalities that could lead to leaking of blood into the eye and hyphema.
- Eye surgery: Eye surgery, also known as ocular surgery, refers to a procedure carried out on the eye and its structures, often to correct vision issues or treat eye conditions such as cataracts. Eye surgery, especially invasive eye surgery, may lead to hyphema if blood vessels in the anterior chamber of the eye are injured.
What are the Symptoms of Eye Bleeding (hyphema)?
The symptoms of eye bleeding or hyphema include blood in the eye, sensitivity to light, eye discomfort and blurry or hazy vision. The exact symptoms of hyphema will depend on what has caused the bleeding in the eye, as will the severity of the hyphema. The possible symptoms of eye bleeding or hyphema are listed below.
- Blood in the eye: Blood in the eye, in regard to hyphema, refers to blood that has gathered in the anterior chamber of the eye and is visible to the naked eye or by slit-lamp examination.
- Sensitivity to light: Sensitivity to light, also known as photophobia, is a condition in which looking at light causes eye discomfort or pain. If hyphema affects the cornea, light sensitivity may be a possible symptom.
- Eye discomfort: Eye discomfort is a possible symptom of hyphema. Eye discomfort is a general term encompassing several feelings, including eye pain and itching.
- Blurry or hazy vision: Blurry or hazy vision may be caused by blood obstructing areas of the eye, such as the pupil, which can occur if a person has hyphema.
1. Blood in the Eye
Hyphema, as a medical term means blood in the eye. Therefore, blood in the eye is not technically a symptom of hyphema but the definition and main clinical sign of the eye condition itself. Blood in the eye, or hyphema, refers to blood that has collected between the iris and the cornea, also known as the anterior chamber of the eye. Hyphema is usually visible to the naked eye or via examination by a slit-lamp, according to James Gragg, Kyle Blair, and Mari B. Baker, in a paper published in the National Library of Medicine. Blood in the eye or hyphema is caused by trauma or injury to the blood vessels in the eye. Blood in the eye or hyphema can also be caused by medical conditions that affect the blood vessels.
2. Sensitivity to Light
Sensitivity to light, also known as photophobia, is a possible symptom of hyphema. Sensitivity to light describes a condition in which light causes discomfort or pain in the eyes. Sensitivity to light as a symptom of hyphema can be due to the way hyphema interferes with or irritates the cornea. The cornea is the window at the front of the eye that allows light in. If hyphema has affected the cornea, it may affect how light is received, making someone more sensitive to light.
If you are experiencing sensitivity to light, it is important to seek medical attention.
3. Eye Discomfort
Eye discomfort is a possible symptom of eye bleeding or hyphema. Eye discomfort is a general term that refers to an uncomfortable feeling in the eye. Eye discomfort may feel like an irritated, itchy feeling in the eye or a throbbing, aching or stabbing eye pain. Eye discomfort in cases of hyphema can be caused by the blood leaking into the anterior chamber, irritating the eye or causing extra pressure in the eye.
4. Blurry or Hazy Vision
Blurry or hazy vision is a possible symptom of hyphema, possibly caused by blood obstructing areas of the eye, such as the pupil or cornea. Blurry vision refers to the vision being unclear and not as sharp as usual, which may make it harder to see. Hazy vision refers to vision that appears cloudy or foggy. Blurry or hazy vision can be a symptom of hyphema if the blood leaking into the anterior chamber of the eye is disturbing the pupil, iris or cornea by covering or obstructing it. The pupil and the iris work together to help a person see objects. If the pupil, iris or cornea is obstructed, it can lead to blurry vision.
When do Eye Bleeding Symptoms Usually Occur?
The symptoms of eye bleeding or hyphema usually occur as soon as the blood vessels in the eye have been affected or damaged and begin to leak. Eye bleeding symptoms, such as blood in the eye, will occur when the blood vessels have been affected, often by injury, trauma or a medical condition, leading to the leaking of blood into the anterior chamber of the eye, which can cause additional symptoms such as eye discomfort and blurry vision.
If you are experiencing blurry vision, it is important to seek medical attention.
What are the Risk Factors for Eye Bleeding (hyphema)?
The risk factors for eye bleeding or hyphema include playing sports, diabetes, blood clotting disorders and certain blood-thinning medications. Some of the possible risk factors for hyphema or bleeding in the eye are listed below.
- Playing sports: Injury or trauma to the eye during sports is one of the top causes of hyphema and, therefore, a major risk factor for developing this condition.
- Diabetes: Diabetes is a risk factor for hyphema as it can cause neovascularisation of the eye, which can lead to spontaneous hyphema.
- Blood clotting disorders: Blood clotting disorders such as haemophilia, sickle cell anaemia and leukaemia are possible risk factors for hyphema.
- Certain blood-thinning medications: Blood-thinning medications may affect how the vessels and blood work in the eye, possibly increasing the risk of hyphema.
1. Playing Sports
Playing sports is one of the most common causes of hyphema, meaning it is also one of the most common risk factors for this condition. Sports are a type of physical activity that includes many different kinds, from soccer to rugby, boxing, baseball and basketball. Sports are a risk factor for hyphema as they often include contact with others, which may include a knock or hit to parts of the face, like the eye area. An injury or trauma to the eye area can damage the blood vessels in the ciliary body and iris, leading to hyphema.
2. Diabetes
Diabetes is a possible risk factor for hyphema or eye bleeding, as it can cause a condition called neovascularisation, which may lead to hyphema. According to the University of Waterloo, diabetes is a medical condition in which the body struggles to convert glucose into energy, leading to high levels of glucose or blood sugar. Diabetes may cause a condition called diabetic retinopathy, in which blood vessels grow abnormally in the eye. Proliferative diabetic retinopathy, in particular, is characterised by neovascularisation, or new blood vessel growth, according to a paper by Cho, Alwassia, Regiatieri, Zhang, Baumal, Waheed, and Duker. A complication of neovascularisation can be hyphema, meaning diabetes is a possible risk factor for hyphema, eye bleeding.
3. Blood Clotting Disorders
Blood clotting disorders are a possible risk factor for hyphema or eye bleeding, as they may lead to blood vessels in the eye leaking, leading to hyphema. Blood clotting disorders refer to conditions in which the blood has trouble clotting. According to Emergency Care BC, blood clotting disorders can lead to thrombosis, in which the blood clots too much, which may block blood flow or haemorrhaging, where the blood doesn't clot enough, leading to bleeding. Blood clotting disorders may pose a possible risk factor for hyphema as they can lead to problems with the blood vessels in the eye, such as leaking, leading to a hyphema.
4. Certain Blood Thinning Medications
Certain blood-thinning medications, also known as anticoagulants, may be a possible risk factor for hyphema. Blood-thinning medications or anticoagulants are types of medication used to prevent blood clots, according to the NHS, and include medications such as warfarin. Blood-thinning medication may affect how the vessels and blood work in the eye, possibly increasing the risk of hyphema.
What are the Eye Bleeding Complications?
The eye bleeding or hyphema complications can include vision loss and glaucoma from hyphema. The possible complications of hyphema are listed below.
- Vision loss: Some vision loss can be a complication of hyphema if the condition is not treated effectively or promptly, and the hyphema is severe in nature. It is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible if you have hyphema to limit complications.
- Glaucoma from hyphema: Glaucoma can be a complication of hyphema due to the blood hindering the drainage system, causing increased intraocular pressure.
Hyphema is a serious condition. It is important to seek immediate medical attention if you believe you may have hyphema.
Does Eye Bleeding (Hyphema) Damage Vision?
Hyphema or eye bleeding does not always damage vision. Depending on the severity and the underlying cause of the hyphema, this condition may be treated without complications to vision. However, if hyphema is not treated promptly, complications such as rebleeding and corneal staining may cause damage to a person's vision.
How does Hyphema Affect Vision?
Hyphema, or eye bleeding, may affect vision by making it blurry or hazy. Hyphema refers to bleeding between the cornea and iris. The cornea is the clear window at the front of the eye that lets light in. The iris is the coloured part of the eye surrounding the pupil. If hyphema bleeding is obstructing the cornea or iris, it may blur vision and make it harder to see.
How is Eye Bleeding Diagnosed?
Eye bleeding is diagnosed by a healthcare or optometry professional, such as an optometrist. The healthcare professional will examine the eye and diagnose accordingly. A slit-lamp test can be used to diagnose hyphema. A slit-lamp test is a high-magnification microscope that can examine the deeper structures of the eye.
Where can you seek an Eye Bleeding Diagnosis?
You can seek an eye bleeding diagnosis from a healthcare or optometry professional. A healthcare professional can include doctors and nurses, found at hospitals or doctors' offices. An optometrist is commonly found at an optometry practice.
What are the Treatments available for Eye Bleeding (hyphema)?
The treatments available for eye bleeding or hyphema depend on what has caused the bleed and how serious the bleed is. A healthcare professional will treat a hyphema and may recommend certain medications to assist in the treatment of hyphema. A healthcare professional may carry out or advise general hyphema or eye bleeding treatments such as elevating the head, resting and covering the eye. Some of the possible treatments for hyphema are listed below.
- Elevating the head: Elevating the head is a way of helping to treat hyphema, as it may help the blood drain out from the eye.
- Resting: Resting is an important part of the treatment process for hyphema, as resting helps to prevent the eye from bleeding again, which can cause complications.
- Covering the eye: An eye care or healthcare professional may advise you to cover the eye as part of treating hyphema, to protect the eye from any further damage.
Hyphema is a serious condition. It is important to seek immediate medical attention if you believe you may have hyphema.
How Many Weeks Does it Take to Recover from Eye Bleeding (hyphema)?
There is no set number of weeks for a hyphema or eye bleeding to recover. Depending on what has caused the hyphema, the severity of the eye bleeding and the treatment that is being received, it may take from a few days to several weeks for a hyphema to heal.
How to Treat Eye Bleeding?
It is important that you do not attempt to treat eye bleeding or hyphema yourself. What to do if your eye is bleeding is to seek immediate medical attention. A healthcare professional will be able to diagnose and treat the condition accordingly.
Can Eye Drops Treat Eye Bleeding?
Eye drops are not generally used to treat hyphema. According to MyHealth Alberta, steroid eye drops may be prescribed to help treat inflammation caused by hyphema, but they will not treat the hyphema itself.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before using eye drops or any other type of medication.
Can Wearing Glasses Protect You From Eye Bleeding (Hyphema)?
Yes, wearing safety glasses may help to protect a person against injuries that may cause hyphema or eye bleeding. Safety glasses refer to a type of protective gear that is worn over the eyes to shield them from foreign objects entering the eye, chemical splashes, the elements, bright lights, or other things that may pose a risk if it comes into contact with the eye. Hyphema, or eye bleeding, is commonly caused by injury or trauma to the blood vessels in the eye. Wearing safety glasses or other protective face wear such as face shields, can help protect the eyes from sustaining injuries that may cause eye bleeding or hyphema.
How to Prevent Eye Bleeding?
As there is not a singular cause for hyphema, the way to prevent eye bleeding depends on the cause of the eye bleeding, such as trauma or specific eye diseases. The ways that may help prevent eye bleeding are to use safety glasses, treat underlying medical conditions, wear headgear when playing sports, follow advice for proper eye care, know the dangers of eye injuries and seek prompt treatment for eye injuries. These preventative measures for eye bleeding and their definitions are listed below.
- Use safety glasses: Using safety glasses helps to prevent hyphema as they may protect the eyes from trauma or injury that may lead to bleeding in the eye.
- Treat underlying medical conditions: Treating underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes, may help to prevent hyphema.
- Wear headgear when playing sports: Wearing headgear when playing sports may help to prevent hyphema, as this protective measure can help limit injury or trauma to the face and eye areas.
- Follow advice for proper eye care: It is important to listen to the advice given by an optometrist or healthcare professional on how to best look after your eyes.
- Know the dangers of eye injuries: Some eye injuries and conditions can be serious and threaten sight. It is important to understand the seriousness of eye injuries and seek prompt medical care if you have bleeding in the eye.
- Seek prompt treatment for eye injuries: Seeking prompt treatment for eye injuries may help prevent eye bleeding or hyphema from becoming serious or leading to long-term complications.
1. Use Safety Glasses
Using safety glasses may help prevent injuries to the eye that may lead to eye bleeding or hyphema. Safety glasses are a type of eyewear that keeps the eyes protected and safe from potential harm or damage. Safety eyewear encompasses a range of eye protection, such as safety glasses, goggles, face masks and face shields, made from a range of materials and can have lenses with different tints. Eye bleeding can be caused by trauma to the eye; therefore, it is important to use safety eyewear when engaging in high-risk activities, when at work or in everyday life, anywhere that potentially hazardous material could come into contact with the eye and cause injury.
2. Treat Underlying Medical Conditions
Eye bleeding or hyphema may be caused by underlying medical conditions such as eye tumours, diabetes, clotting disorders or sickle cell disease. Therefore, treating these medical conditions may help prevent eye bleeding. People with these medical conditions may be predisposed to issues such as vascular abnormalities, which may lead to blood leaking into the eye and hyphema. Treatments for these conditions may include surgery for eye tumours and medication for diabetes.
3. Wear Headgear When Playing Sports
Wearing headgear when playing certain sports, such as football, is a way to help prevent injuries that may cause eye bleeding. Headgear and helmets should fit comfortably but snugly on the head so that they don't fall off or restrict blood flow. As eye bleeding can be caused by trauma or injury to the eye or face, which is known as hyphema, headgear may offer eye and face protection and can help prevent eye bleeding. Headgear not only may prevent eye bleeding, but it also protects the person's eyes and safeguards them from cuts.
4. Follow Advice for Proper Eye Care
It is important to follow advice for proper eye care to help prevent hyphemas, such as wearing headgear and other eye protective gear, such as safety goggles and glasses, to help protect the eyes and prevent hyphema. Your optometrist may also provide advice on how to prevent hyphema, such as getting regular eye exams.
5. Know the Dangers of Eye Injuries
Knowing the dangers of eye injuries is an important way to look after your eyes. Some eye injuries can be serious and sight-threatening if left untreated. It is important to understand this and to seek immediate medical assistance for any eye injuries, including hyphema, to prevent any complications.
6. Seek Prompt Treatment for Eye Injuries
It is important to seek prompt treatment for eye injuries as it may prevent eye bleeding or prevent it from getting worse. Even if you don't think the eye injury is serious, it should be assessed by a medical professional, as there may be complications not visible or you may be presenting with symptoms that are more serious than you realise.
Is Eye Bleeding (hyphema) an Emergency?
Eye bleeding or hyphema can be classified as an emergency, as the condition can be a threat to vision if not treated promptly. It is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible if you have eye bleeding.
What are the Other Types of Eye Bleeding?
There are several other types of eye bleeding besides hyphema, including subconjunctival haemorrhage, haemolacria, subretinal haemorrhage and vitreous haemorrhage. The different eye bleeding types are listed below.
- Subconjunctival haemorrhage: A subconjunctival haemorrhage refers to eye bleeding that occurs under the conjunctiva, or surface of the eye.
- Haemolacria: Haemolacria is a rare condition in which the tears of the eyes have blood in them.
- Subretinal haemorrhage: Subretinal haemorrhage refers to bleeding in the retinal area.
- Vitreous haemorrhage: Vitreous haemorrhage refers to bleeding in the vitreous cavity.
1. Subconjunctival Haemorrhage
A subconjunctival haemorrhage refers to a type of eye bleeding that occurs under the conjunctiva, which is the membrane that covers the surface of the eye and the eyelids. A subconjunctival haemorrhage occurs when blood vessels break under the conjunctiva, leading to the conjunctiva turning red. Causes of subconjunctival haemorrhages include movements or activities that strain the eyes and the area around the eyes, such as coughing or sneezing, as well as injuries to the eye.
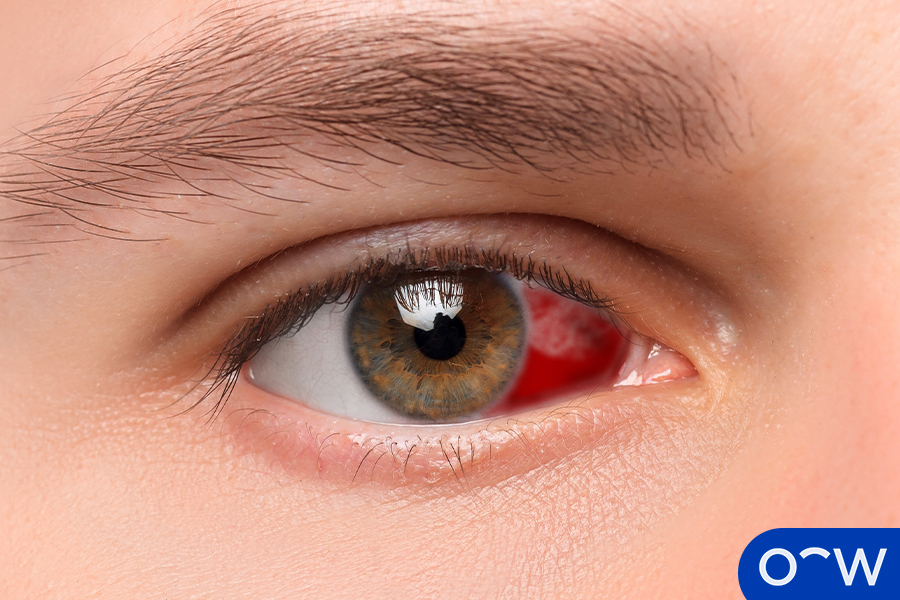

2. Haemolacria
Haemolacria is a rare condition characterised by the presence of blood in the tears. According to Tripathy K and Salini B in a paper for the National Library of Medicine, there are a variety of causes of haemolacria, including bleeding under the conjunctiva, vascular lesions, inflammation, infection or trauma.
3. Subretinal Haemorrhage
A subretinal haemorrhage refers to bleeding under the retina, near the macula. Subretinal haemorrhaging may be found in cases of wet macular degeneration and can be caused by choroidal blood vessels in the retina, according to the University of Michigan.
4. Vitreous Haemorrhage
Vitreous haemorrhaging refers to bleeding in the vitreous cavity. According to MyHealth Alberta, vitreous humour is the substance that fills the eyeball, which is clear and jelly-like in texture. A vitreous haemorrhage can have a variety of causes, such as trauma, tumours or neovascular age-related macular degeneration, according to Jena and Tripathy from the National Library of Medicine.
What is the Difference Between Hyphema and Subconjunctival Haemorrhage?
Both hyphema and subconjunctival haemorrhage refer to bleeding in the eye; however, the difference between hyphema and a subconjunctival haemorrhage is the location of the bleeding. Hyphema is bleeding in the eye, specifically in the anterior chamber between the cornea and the iris. Hyphema can be caused by injury or trauma to the eye or medical conditions. A subconjunctival haemorrhage refers to bleeding under the conjunctiva, the membrane that covers the surface of the eye and inner eyelids. A subconjunctival haemorrhage can be caused by straining due to coughing or sneezing or eye injuries.
Hyphema is a serious condition. It is important to seek immediate medical attention if you believe you have a hyphema or any other bleeding in the eye.
Read Eye Bleeding (Hyphema): Definition, Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors and Treatment in other Oscar Wylee regions and their languages.
 Canada
Canada




